Elevated Recession Probabilities
Recently, J.P. Morgan Research raised the likelihood of a U.S. and global recession occurring before the end of 2024 to 35%, up from a previous estimate of 25%. This increase in probability is not just a number; it reflects growing concerns about the global economic landscape. Factors such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and inflationary pressures contribute to this heightened risk. For individuals and businesses alike, these statistics serve as a wake-up call to reassess financial strategies and prepare for potential economic challenges.
German Economic Contraction
Germany, known for its robust economy, is now facing a period of contraction. In the fourth quarter of 2024, Germany’s economy shrank by 0.2%, sparking fears of another recession in Europe’s largest economy. This contraction is significant because Germany plays a pivotal role in the European Union’s economic health. A slowdown here can have ripple effects across the continent, impacting trade, investment, and employment. The situation highlights the interconnectedness of global economies, where a hiccup in one region can lead to broader economic concerns.
Global Debt Concerns
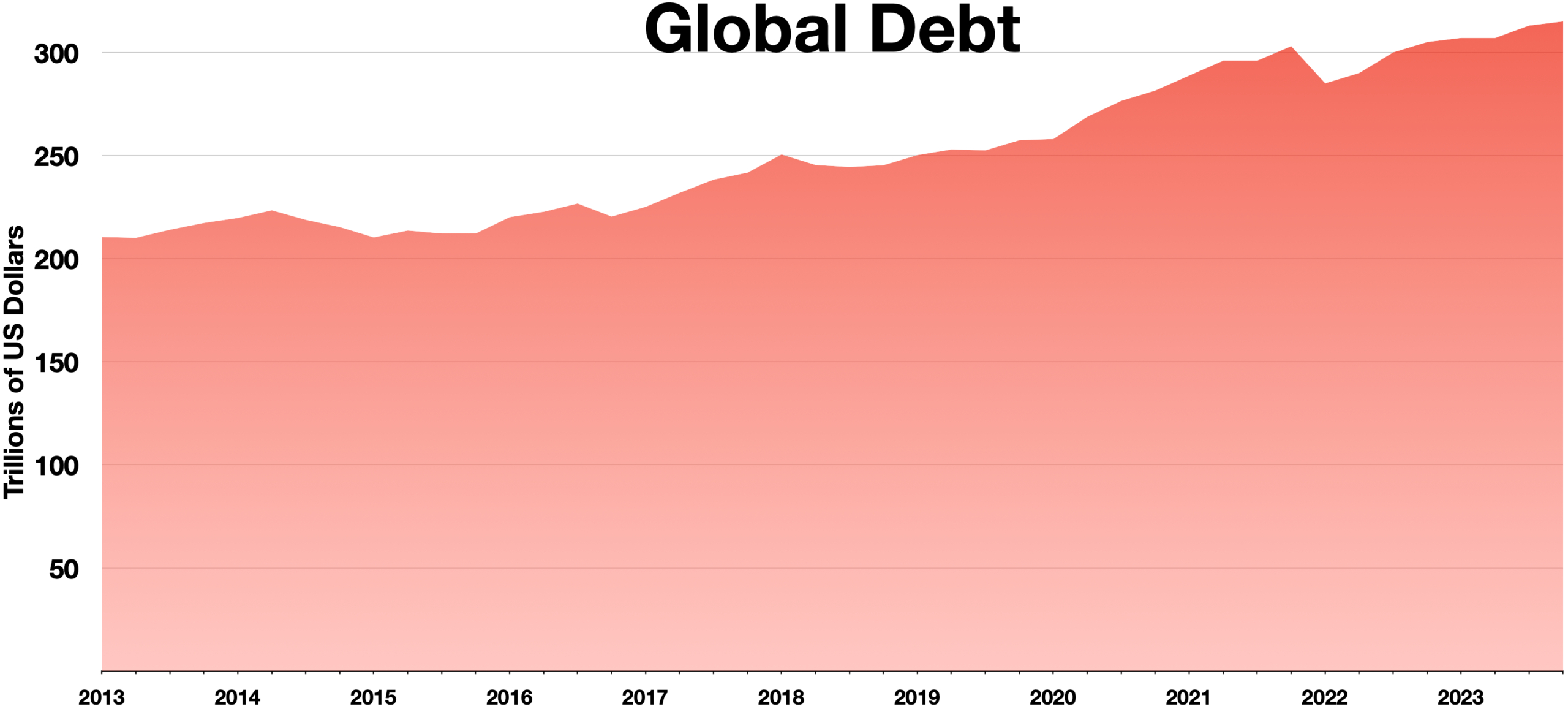
The world is grappling with an unprecedented level of debt, estimated at a staggering $102 trillion last year. Such high levels of global debt are a cause for concern among economists, as they can trigger financial crises if left unchecked. Debt, when managed poorly, can become a ticking time bomb, waiting to explode in the face of economic downturns. This situation urges governments and financial institutions to address underlying issues and implement sustainable debt management practices to prevent potential catastrophes.
Key Recession Indicators
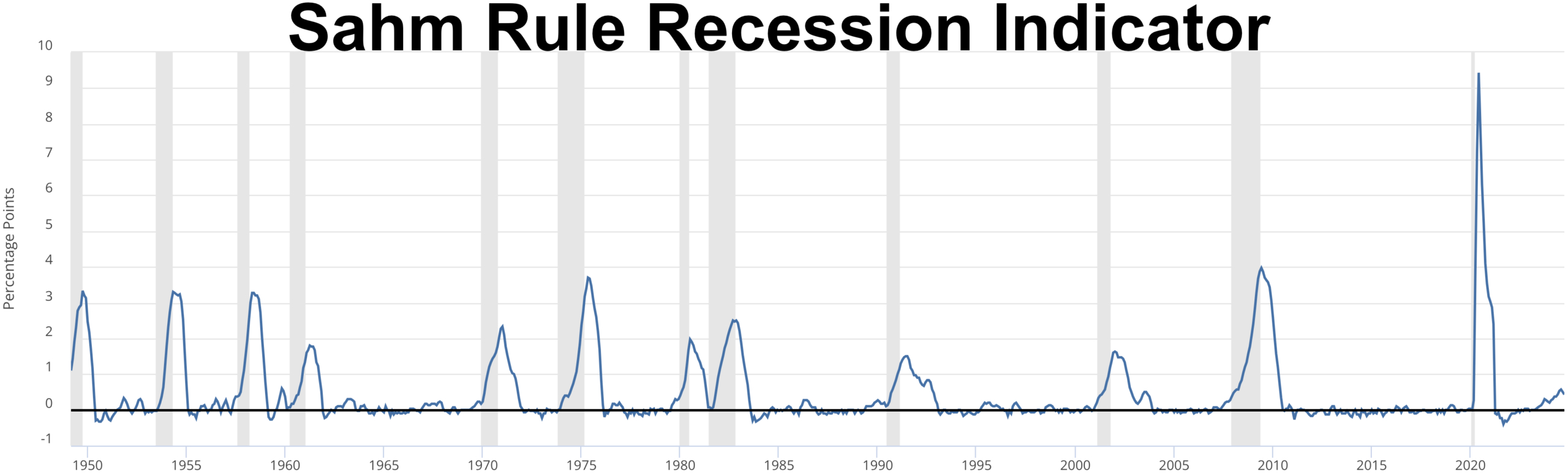
Economists employ several indicators to gauge the risk of a recession. Inflation rates, stock market performance, credit spreads, and yield curve inversions are some of the critical metrics they monitor. For instance, a yield curve inversion, where short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, has historically been a reliable predictor of recessions. By keeping an eye on these indicators, individuals and businesses can better understand the economic climate and make informed decisions. It’s akin to reading weather patterns to prepare for a storm; being forewarned allows for better readiness.
Impact on Employment
Recessions often lead to higher unemployment rates, posing significant challenges for job seekers, including recent graduates. As companies tighten their belts, hiring freezes and layoffs become common, making the job market more competitive. This reality underscores the importance of having a robust skill set and being adaptable to changing industry needs. For those already employed, maintaining professional development and networking can be crucial in safeguarding one’s career during uncertain times.
Building an Emergency Fund
One of the most practical steps individuals can take to brace for a recession is to establish an emergency fund. Financial advisors typically recommend setting aside enough to cover 3-6 months of living expenses. This fund acts as a financial cushion, providing peace of mind and stability in case of income disruptions. Just as a parachute is essential for safety when skydiving, an emergency fund is vital for navigating the uncertainties of a recession. It allows individuals to weather financial storms without resorting to high-interest debt or drastic lifestyle changes.
Managing Debt
Reducing personal debt is another crucial strategy for mitigating financial stress during economic downturns. High debt levels can quickly become overwhelming if income decreases, making it essential to address outstanding balances proactively. Individuals should focus on paying down high-interest debt first and consider consolidating loans to lower interest rates. By managing debt effectively, individuals can free up resources and improve their financial resilience, much like shedding extra weight to run faster in a race.
Investment Strategy
Maintaining a diversified investment portfolio is a key strategy for navigating market volatility during recessions. Diversification spreads risk across various asset classes, reducing the impact of a downturn in any one area. Investors are encouraged to focus on long-term financial goals rather than reacting impulsively to short-term market fluctuations. This approach is akin to steering a ship through stormy seas; a steady hand and clear direction ensure that one reaches the intended destination safely, despite the turbulence along the way.



